52: Mathematics
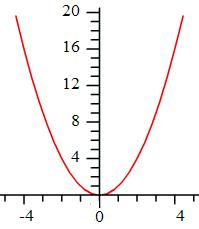
One is the square of one and is zero plus the first odd number. Each successive square is the previous square plus each successive odd number. The first odd is one plus zero, and each successive odd is each corresponding natural number plus the previous. In general, x plus x minus one, or two x minus one. Putting these observations together, we can generate the series of squares with a series of simple additions— The square of x, where x is the series of natural numbers, is the square of one less than x plus the corresponding odd, two x minus one: x2 = (x - 1)2 + (2x - 1). This equation tells us the relations between the natural numbers, the odd numbers, and the squares. Further, when transposed to a Cartesian grid and the real numbers (positive and negative), it traces out a conic section, the parabola whose apex is at the center, and whose left and right arms reach upward to infinity.