Christian Doppler
physics
|
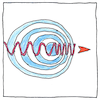
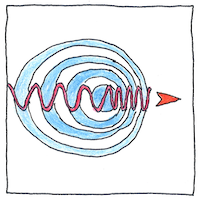
Doppler effect
Doppler proposed that the drop in pitch that he perceived listening to a truck of trumpeters on a train passing by him was proportional to the velocity of the train. Approaching, the trumpeters sounded sharp; receding, they sounded flat. If the train were faster, he said, they would have sounded even sharper approaching and even flatter receding. The frequency of any wave-like phenomenon such as light or electromagnetic radio waves produced from an object moving in relation to an observer is affected by the relative velocity between the object and the observer. This explains the redshift in the light of stars as they recede toward the edges of the universe and the flatness of the sound of trumpets as they recede from our listening ears.
Sans relativity
Relativity and the foreshortening of matter as it approaches the speed of light in physicists’ thought experiments as though matter like light were a form of wave wouldn’t be invented until much later.
Effects
The Doppler effect is only a small part of the great summation of effects that includes the John Doe effect by which every customer approaches anonymity relative to the number of customers and the Bulwar-Lytton effect by which every writer approaches mediocrity relative to amount of his or her output.


Christian Doppler described the effect in his treatise “Über das farbige Licht der Doppelsterne und einiger anderer Gestirne des Himmels—Versuch einer das Bradley’sche Aberrations-Theorem als integrirenden Theil in sich schliessenden allgemeineren Theorie” (On the coloured light of the binary stars and some other stars of the heavens—Attempt at a general theory including Bradley’s theorem as an integral part), which has a fairly descriptive title. He used the Doppler effect to explain the color of binary stars.
Doppler is not recognized as the father of relativity. Albert Einstein used the Doppler-shift factor to help establish the equivalence of mass and energy in 1905 and reformulated the Doppler effect to account for the time dilation effect of the special theory of relativity.
See also in The book of science:
Readings in wikipedia: