Frederick Soddy,
Kazimierz Fajans
physics

|
Radioactive displacement law
When a radioactive isotope spontaneously transmutes then it may emit a helium nucleus or an electron and an electron antineutrino. Ernest Rutherford called the first type “alpha decay”; and the second type “beta decay.” Now we call the second type “beta minus decay.” The Fajans and Soddy radioactive displacement law tells you what element or isotope the decay results in. Alpha decay creates an element with two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons. Beta decay creates an isotope with one additional proton and one fewer neutron.
Other forms of decay
Other forms of radioactive decay. “Beta positive decay” when the isotope emits a positron and an electron neutrino. This is also called “positron emission.” Irène and Frédéric Joliot-Curie induced it and called it “artificial radioactivity.” “Electron capture” when the nucleus captures an electron and emits a neutrino. “Proton emission” when the nucleus emits a proton. “Neutron emission” when the nucleus emits a neutron.
Transmutation
Alchemists failed to transmute base elements to gold, leading many to think it was impossible. Beyond their means and beyond their knowledge but not beyond the possible since it had happened in the stars.
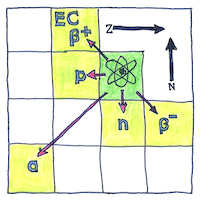


Soddy and Fajans had begun to stabilize the idea that elements could be unstable. When atoms lose subatomic particles, they do so according to certain rules.
See also in The book of science:
Readings in wikipedia: