Kristian Birkeland,
Carl Størmer,
James Van Allen
electromagnetism

|
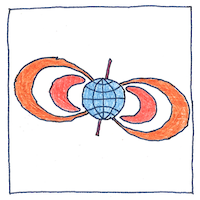
Van Allen belts
Kristian Birkeland ran expeditions to northern Norway and established a network of observatories to see how the magnetic field related to the northern lights. He proposed in 1908 that Earth’s magnetic field guided electrons ejected from the sun toward the poles where they interacted with currents, now known as Birkeland currents, that flow along geomagnetic field lines from the north pole. Birkeland’s theories were ridiculed until rockets were deployed to permit direct measurements from space. * Birkeland died in 1917 but Carl Størmer was inspired by Birkeland to study the motion of charged particles in Earth’s magnetosphere and develop mathematical models of them, predicting orbits of charged particles that were later confirmed by James Van Allen. * James Van Allen designed the scientific instrumentation for Explorer 1, the first satellite launched by the United States, and the first spacecraft to detect a Van Allen radiation belt. Van Allen’s instrumentation included an omnidirectional Geiger-Müller tube to detect cosmic rays five temperature sensors an acoustic detector and a wire grid detector to detect impacts of cosmic dust packed into a cone and cylinder a yard long and six inches in diameter. Charged particles trapped by Earth’s magnetic field overwhelmed the Geiger counter so that it read zero as Explorer 1 passed through the inner Van Allen belt.
Shields
The inner Van Allen belt contains mainly high-energy electrons trapped by earth’s magnetic field. The outer Van Allen belt contains high-energy electrons and ions and fluctuates in response to geomagnetic storms. A transient third belt just outside the atmosphere contains unrelativistic particles that merge with the outer belt. Van Allen belts protect the atmosphere against the solar wind; however, charged particles in the belts cause problems for satellites.
Auroras
Winds of charged particles from the sun batter the magnetosphere of the earth so both rain charged particles into the upper atmosphere at high latitudes. which excites atmospheric gases to emit a diffuse glow or folded curtains of light red from atomic oxygen at high altitudes green at lower altitudes from nitrogen transfering energy to oxygen blue and red from nitrogen at lower altitudes combine for yellow and pink.


Galileo named the northern lights Aurora Borealis in 1619. The same phenomenon near the south pole is called Aurora Australis. Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune also get auroras.
Without a molten core, Earth would have no magnetic field, no aurora, and no atmosphere, like Mars.
See also in The book of science:
Readings in wikipedia: