Fritz Haber
chemistry
|
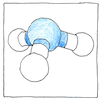
Synthesis of ammonia
Nitrogen is the most abundant element in our atmosphere and is essential for life; however, its gaseous diatomic form is inert. Ammonia is composed of one part nitrogen and three parts hydrogen but if you combine nitrogen gas with hydrogen nothing happens. Plants harbor an enzyme in a bacterium to break nitrogen-nitrogen bonds to convert nitrogen gas to ammonia or nitrate. Before an efficient industrial process was available, nitrate or ammonia was extracted from camel dung, and from the distillation of coal, and by the decomposition of natural ammonium salts. Fritz Haber discovered that iron filings worked as a catalyst, producing ammonia, and by increasing heat and pressure managed to increase the yield to six percent. Six percent was commercially viable, especially when the unreacted nitrogen and hydrogen gases could be recirculated over and over.
Fertilizer, bombs, and other uses
Cleaner Disinfectant Explosive Fertilizer Lifting gas Refrigerant Rocket fuel Stimulant
Irritant
A colorless and irritating gas with an acrid odor, ammonia is corrosive when mixed with water, and can burn the skin, cause blindness, brain damage, lung damage, or death.
Ethics
In World War I, the Germans had no shortage of ammonia for bombs and rocket fuel due to Fritz Haber, a Jew. Haber also worked hard to develop chemical weapons for the Germans, leading the teams that developed chlorine gas and gas masks, and personally overseeing the first gas releases on the front lines. In the twenties, at Haber’s institute, scientists developed the cyanide gas Zyclon A, which the Nazis modified and used to murder Jews in concentration camps during the Holocaust. Both his wife Clara and his son Hermann committed suicide over their conflicts with his work on chemical warefare agents.
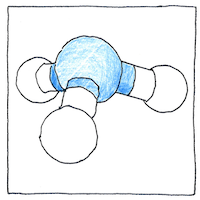


All organic life, animal and plant, relies on trace amounts of water-soluble nitrogen. We do not get it by breathing air, which contains 78.09% diatomic nitrogen gas. Bacteria in the digestive tract break down proteins into nitrogen compounds including ammonia. The liver removes extra ammonia from the bloodstream by converting it to urea which is released from the body in urine.
See also in The book of science:
Readings in wikipedia: